Life insurance is an important part of financial planning, but choosing which type to get will depend on several factors. For example, many Canadians look into permanent (aka whole) life insurance for its lifelong coverage and cash value, but the high costs and complexity can make it less appealing than other options.
Is permanent life insurance the right choice for you? Keep reading to explore who benefits from permanent life insurance, its potential downsides, alternative options, and real-life case studies to help you decide.
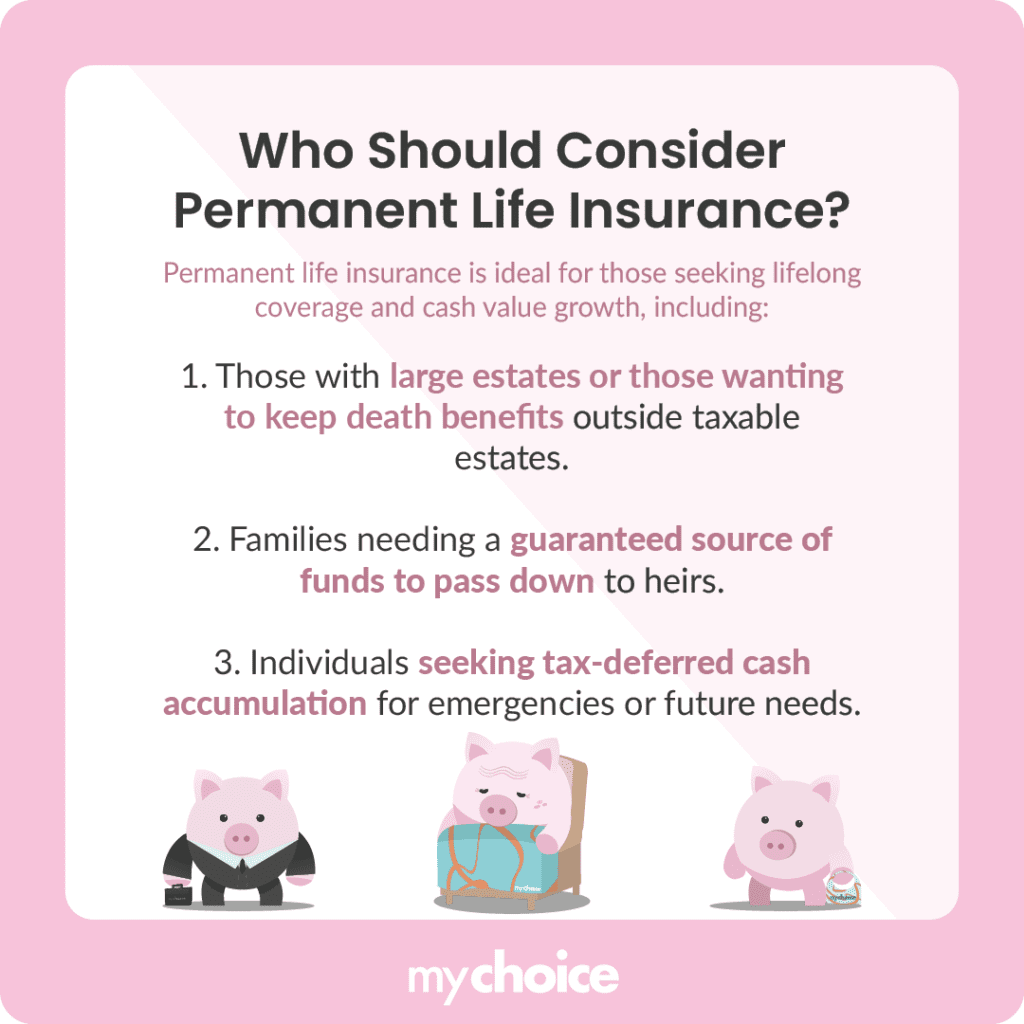
Who Is Permanent Life Insurance For?
Permanent life insurance is best suited for those who need lifelong coverage and want to build cash value as part of their long-term financial strategy, such as adding a return of premium to their policy.
It’s often marketed to the following people:
What Are the Downsides of Permanent Life Insurance?
While permanent life insurance has its advantages, it also comes with some notable drawbacks:
What Are the Alternatives?
If permanent life insurance doesn’t fit your needs, here are some other options worth considering:
Here’s a quick comparison of permanent and term life insurance to give you a clearer picture:
| Feature | Permanent Life Insurance | Term Life Insurance | Universal Life Insurance | Guaranteed Life Insurance | Variable Life Insurance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premiums | High, fixed for life | Lower, fixed for the term period | Flexible (can increase or decrease) | Typically higher due to guaranteed acceptance, often fixed | Varies; can be higher due to the investment component |
| Coverage Duration | Lifetime | Specified Period (e.g. 10,20, or 30 years) | Lifetime | Lifetime | Lifetime |
| Cash Value | Yes, accumulates over time | No cash value component | Yes, accrues over time based on credited interest | Minimal or none | Yes, grows or shrinks with market performance |
| Flexibility | Limited adjustments allowed | Greater flexibility with renewals | High (can adjust premiums and death benefit within certain limits) | Low; coverage amounts are usually modest and fixed | Moderate; can choose investment options, but returns depend on market performance |
Real-Life Scenarios & Case Studies
Understanding your coverage options is easier when you see how they apply to different life stages. Here’s how different individuals might approach life insurance:
Key Advice From MyChoice
- Note your outstanding debts and future obligations (like mortgage payments) before deciding which policy to get, as this influences how much coverage you may need and can afford.
- Some policies are more adaptable than others, so consider options that can adjust as your life changes. A flexible plan now can save you from scrambling for additional coverage later.
- Consult a trusted advisor. A little professional guidance can go a long way in helping you make a confident, informed decision. Look for someone who prioritizes your needs rather than just making a sale – transparency and expertise are key.