Modern-day businesses require risk management strategies and due diligence to protect companies from unforeseen events. One essential tool is the Certificate of Insurance (COI), which provides proof of coverage, fosters trust, and safeguards both parties during contractual relationships.
What does a COI do for your business? Do COIs differ from province to province? When is a COI relevant to your company? Read on to learn about why these certificates are relevant to modern businesses and how you can acquire or renew your COI.
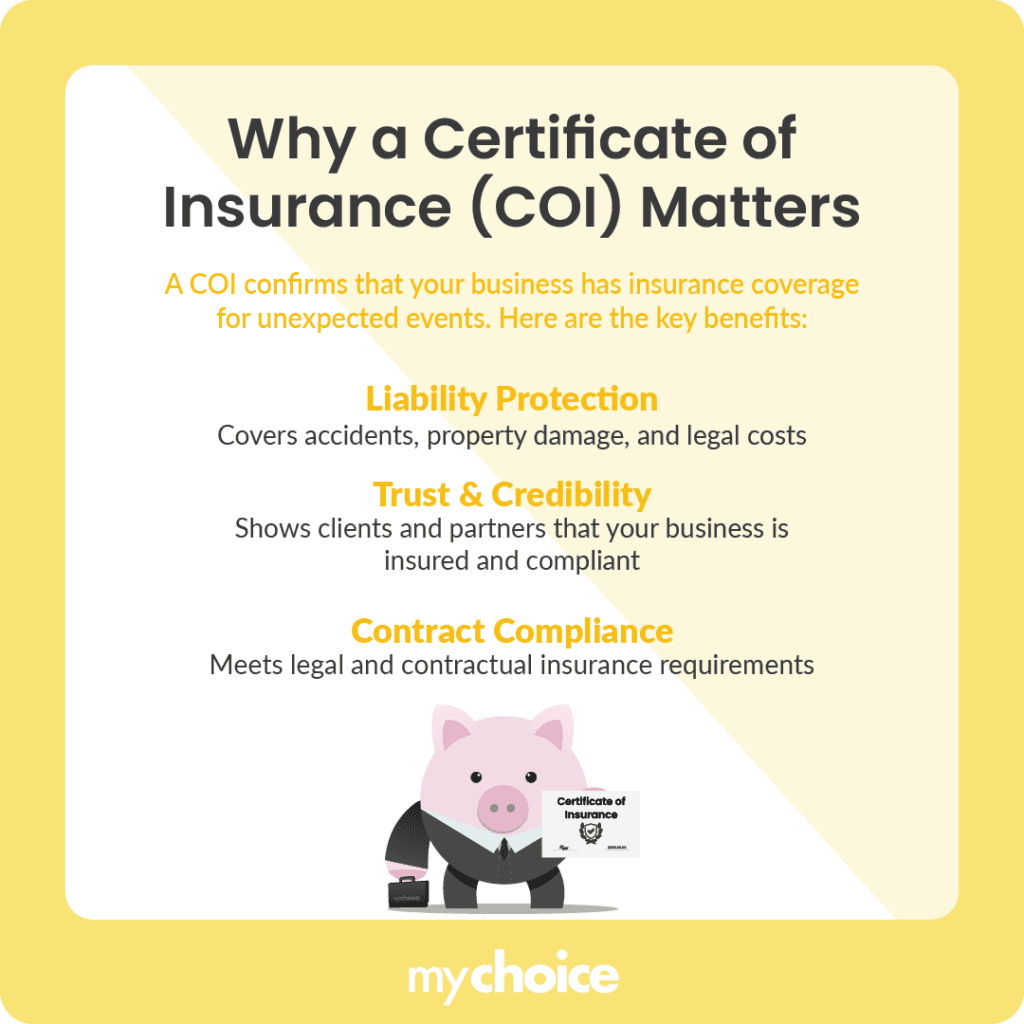
Why is a Certificate of Insurance (COI) Important for Your Business?
A COI proves that your business has the necessary insurance coverage in place should an unexpected event occur. This is important for a few reasons:
Types of Certificates of Insurance
These are some of the most popular types of COIs:
Provincial Variations
Each province in Canada handles insurance differently from the other provinces. This means that COIs in each province can have slight variations depending on the specific provincial regulations and guidelines.
How to Get/Renew My Certificate of Insurance
Obtaining and renewing your COI is a simple process. If you own a business, you will likely already have this document available. However, if you want to get a new or updated copy, these are the steps you’ll need to take:
- Review your policy details: Go through your insurance policy to ensure that it’s up to date and that all details are correct. Any discrepancies can lead to issues when a client or partner reviews your COI.
- Add an additional insured: If needed, name an entity as an additional insured under your policy. This provides coverage for outside parties working with you or on your property and typically only for a specified time period.
- Request the certificate: Once your policy details have been reviewed and any additional insured parties have been added to your policy, ask your provider to issue or renew your COI. The document will be sent directly to you or your designated business partner, meeting the requirements stipulated in your contract or agreement.
How Long Does It Take to Obtain a COI?
Obtaining a COI can take anywhere between a few days to a few weeks.
To speed up the process of obtaining a COI, make sure you have all the necessary information on hand when contacting your broker.
How Long Is a COI Good For?
A COI is usually valid for as long as your policy is active. However, this is not always the case. Typically, a COI can last up to five years.
Scenarios Where a COI Saves the Day
Having a Certificate of Insurance allows businesses to prove to other entities that they have adequate coverage for any liability claims that may arise. Here are a few situations where a COI can come to the rescue:
How to Verify Another Party’s COI
Verifying another party’s Certificate of Insurance is essential in establishing trust and ensuring that all contractual obligations are met. Here’s how you can confirm the validity of a COI:
- Review the certificate details: Carefully examine the COI for key elements such as the policy number, coverage limits, and effective dates.
- Contact the issuing insurance company: Reach out directly to the insurance provider listed on the COI. They can confirm whether the policy is active and meets the requirements outlined in your contract.
- Check for endorsements or exclusions: Ensure that the certificate does not include any endorsements or exclusions that might reduce the coverage in ways that could impact your risk management strategy.
Key Advice from MyChoice
- Regularly review and update your insurance documentation to remain prepared if you need to present it. Keeping your COI current demonstrates to partners and clients that your business is committed to risk management.
- Establish a systematic process for renewing your COI and verifying the certificates of potential business partners to avoid delays and disruptions in your operations.
- Take the time to understand your insurance policy’s terms and limitations thoroughly. Knowing exactly what is covered and what isn’t allows you to address any potential gaps before they become liabilities.