Life expectancy in Canada has increased dramatically over the past century, reflecting advances in healthcare, improved nutrition, and a strong social safety net. Today, many Canadians can reasonably expect to live into their 80s or beyond, an achievement that also poses unique challenges for businesses and government agencies. In the insurance sector, for instance, longer lives require constant recalibration. Insurers must adapt policies, premiums, and risk models to an aging population that remains active and engaged well into later life.
How much did Canada’s life expectancy improve over the past century? Is the life expectancy the same for every province? How about for men and women? Read on to learn about the factors that affect Canadian life expectancy and how this longer lifespan can affect insurance products.
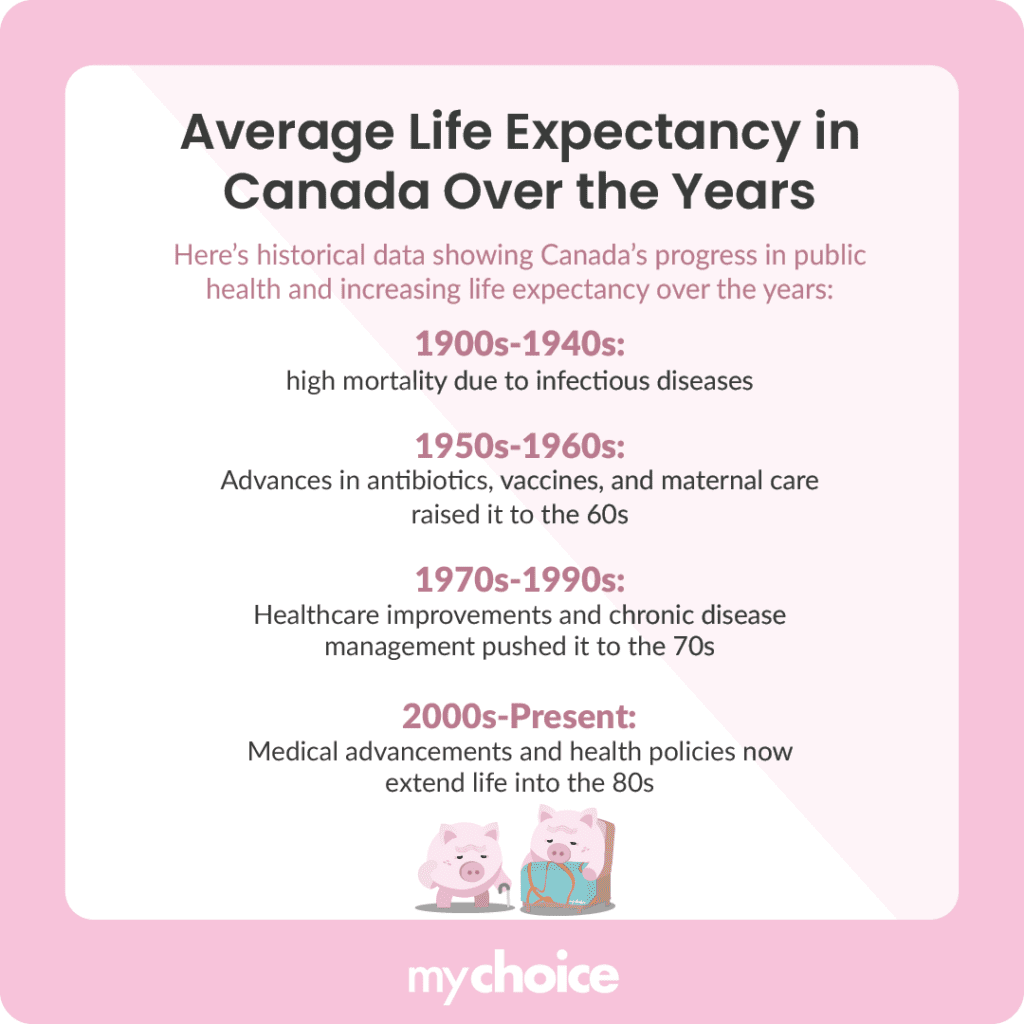
Average Life Expectancy in Canada Over the Years
Thanks to historical data, we can see how far Canada has come in terms of public health and standard of living. Here’s how the life expectancy rate has risen over the years:
Regional Variations
Despite Canada’s universally admired healthcare system and overall high living standards, life expectancy figures do exhibit notable regional variations. These disparities are often due to differences in demographics, economies, and access to specialized healthcare services across the country. Here’s how the life expectancy can differ throughout the provinces:
Life Expectancy in Canada: Men vs Women
Across the globe, there is a consistent phenomenon that women tend to live longer than men. While this is also true for Canada, the life expectancy gap is slightly narrower than the global average. Globally, the life expectancy gap between men and women is five years. In Canada, the gap is only four years, with men living to 80 years and women living to 84 years on average.
Impact of Rising Life Expectancy on Life Insurance
The rise in life expectancy is a positive for all Canadians. However, it does have some implications for both insurers and policyholders. As people live longer, insurance companies must adjust their products and pricing to maintain sustainability. Here are some ways that an extended lifespan affects insurance companies:
Key Advice From MyChoice
- Buying a life insurance policy at a younger age will allow you to get a good annual premium compared to buying life insurance later in life.
- Review your life insurance policy regularly and adjust your coverage as you move through different life stages.
- If you are concerned about critical illness, disability, or long-term care, you can add riders to your life insurance policy.