Life insurance for Canadians is generally not tax-deductible. However, there may be certain scenarios where you can get a tax deduction on your policy.
When is life insurance in Canada tax-deductible, and are life insurance tax policies the same across different provinces? Keep reading to find out.
When Is Life Insurance Tax-Deductible?
According to Canada’s Income Tax Act (ITA), individual life insurance premiums aren’t generally tax-deductible. However, there are specific scenarios where group life insurance paid by businesses becomes tax-deductible.
Here’s how you can make life insurance premiums tax-deductible if you’re a business owner:
- You must include life insurance as part of your employee benefits.
- You must not benefit from the policy, meaning only the employee and their loved ones benefit from it.
If you fulfill those two conditions, your life insurance payments become tax-deductible as business expenses.
Why Aren’t Life Insurance Premiums in Canada Tax-Deductible?
Life insurance premiums in Canada are generally considered personal expenses, so they can’t get tax deductions. You already get tax benefits because life insurance payouts aren’t taxable. So, you can say that in most cases, life insurance’s tax benefits come later when the policy pays out and not while you’re still paying for it.
How Does Life Insurance Taxation Differ Across Provinces?
Life insurance taxation in Canada generally differs slightly across provinces. There are federal tax rules that apply to the entire country, but there are also some differences between provinces that depend on each province’s regulations. For example, you may encounter retail sales taxes when paying insurance premiums in Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec.
You can ask a tax professional for detailed information about life insurance taxation differences in various Canadian provinces.
An Overview of Life Insurance’s Tax Implications
We’ve covered above that life insurance premiums in Canada usually aren’t tax-deductible. However, life insurance payouts aren’t counted as taxable income, meaning your beneficiaries will receive that payout without tax cuts. But if you have life insurance with an investment or cash value component, that part of the policy may be subject to taxation.
For a clearer understanding of which elements of life insurance are subject to tax and which are not, let’s break it down in a table:
| Life Insurance Component | Tax Treatment |
|---|---|
| Premium payments | Not tax-deductible for individuals, tax-deductible for business owners if you fulfill the conditions. |
| Cash value growth | Grows on a tax-deferred basis, so you don’t have to pay taxes on it as long as the policy is active. |
| Death benefits | Generally tax-free, meaning your beneficiaries receive the full amount without tax cuts. |
| Policy loans | Generally not taxable. |
| Cash value withdrawals | May be taxable, depending on how much you withdraw. |
Exceptions on Death Benefit Taxation
While death benefits are most often not taxable, there are exceptions. Here are some scenarios that may lead to a death benefit payout to become subject to tax:
- The life insurance policy is owned by a company that also acts as its beneficiary.
- The policyholder used the policy as a loan collateral.
If you’re unsure whether your death benefit will be taxed, talk to a tax advisor.
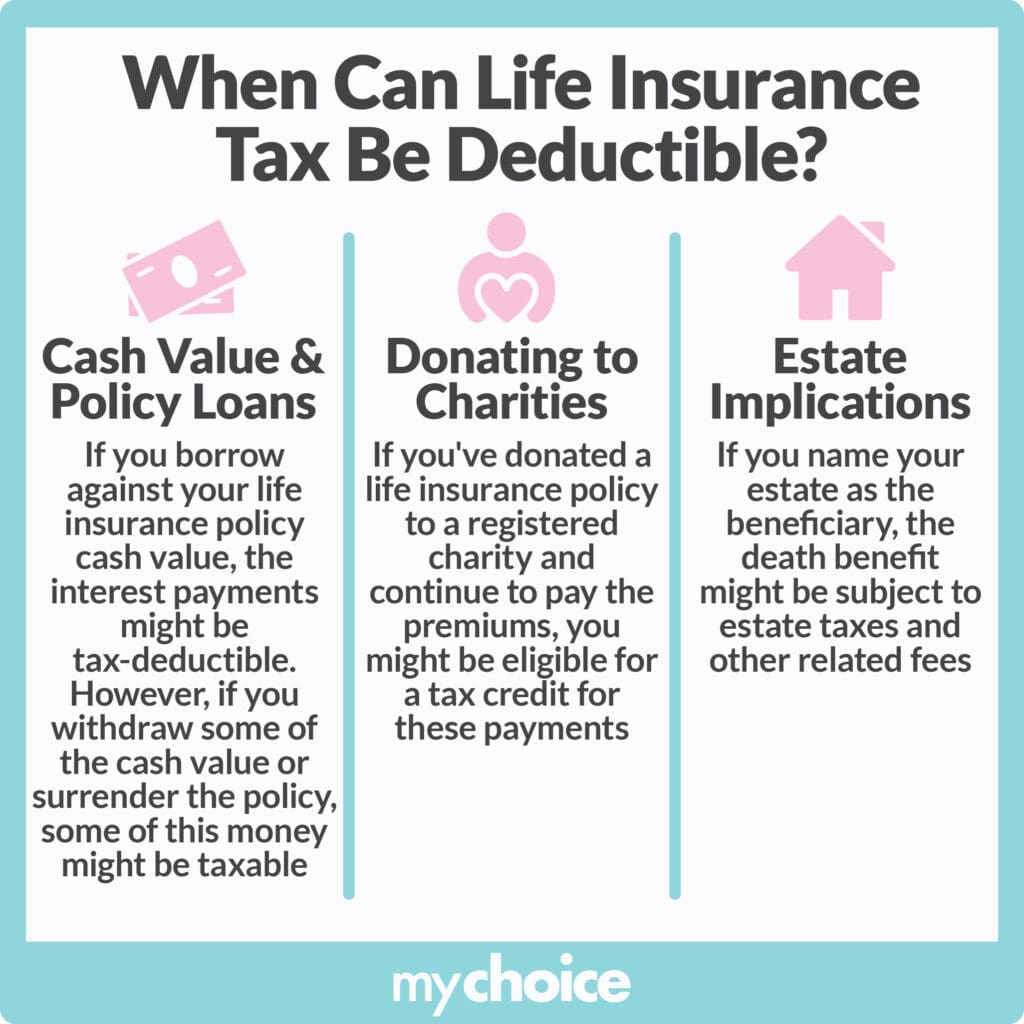
Maximizing Life Insurance Tax Benefits
Life insurance premium payments aren’t tax-deductible. However, that doesn’t mean you don’t have any tax benefits from life insurance. You can gain tax benefits through different ways, such as:
Key Advice From MyChoice
Now that we’ve learned about whether life insurance policies in Canada are tax-deductible, here are some important things to remember:
- Life insurance premiums are generally not tax-deductible because they’re considered personal expenses. The tax benefits on life insurance come later, when the policy pays out, because your beneficiaries will receive the money free of tax.
- Premium payments are generally not tax-deductible if you have a personal life insurance policy.
- If you’re a business owner, you can get tax benefits on your employees’ life insurance premium payments as long as you don’t benefit from the policy since they become business expenses.
- While federal tax rules govern life insurance taxation for the whole country, local regulations may cause different tax rates in different provinces. Contact a tax professional for help navigating the insurance tax landscape in each province.
- Life insurance death benefits generally aren’t taxable, meaning your beneficiaries will get the full amount. However, company-owned life insurance policies may be subject to tax if the company is also the beneficiary. Your death benefit payout may also be taxed if you use the policy as loan collateral.
- While life insurance tax deductions are only available in very specific scenarios, you can gain other tax benefits by using your policy as