When you’re in the market for a new car, you might consider buying an electric or hybrid vehicle. Compared to traditional gas-powered cars, these vehicles are cleaner, safer, and more advanced, making them a great option for drivers who think about their future. However, there are some big differences and considerations between these two types of electrically powered cars, and knowing the pros and cons can help you make the best decision for your situation.
What are the pros and cons of hybrid and electric vehicles? How does owning a battery-powered car affect your insurance premiums? Read on to learn about the differences between hybrid and electric cars and which option is better for you.
The Key Difference Between Hybrid vs Electric Cars
While both of these car types run on electricity, there’s one important factor that differentiates them. Electric vehicles – or EVs – function solely on battery power, while hybrid vehicles have both a battery and an internal combustion engine (ICE) that runs on traditional gasoline. This means that hybrid vehicles are a bit more reliable than purely electric cars, thanks to the gas engine acting as a backup in case the battery runs out.
Car Insurance Considerations
In Ontario, electric vehicle and hybrid owners should consider specific insurance coverages and endorsements that cater to the unique features of their vehicles. These coverages address the distinct needs arising from advanced technology and infrastructure associated with EVs.
Unlike traditional vehicles, EVs may require towing to charging stations rather than conventional repair shops. Insurance providers in Ontario often offer tailored roadside assistance that includes battery jump-starts, charging station location services, and flatbed towing to ensure that EV owners receive appropriate support in case of a breakdown. This coverage can provide peace of mind, knowing that help is readily available, especially during long trips where charging stations may be sparse.
For many electric and hybrid vehicle owners, installing a home charging station is a necessity. Because of this, some insurance companies offer policies that include endorsements to protect home charging equipment against damage or theft. This coverage can be added to a homeowner’s insurance policy, not the auto insurance policy, since the charging equipment is installed in the home. Given how expensive installing a home charging station can be, this type of coverage can help protect electric and hybrid car owners from unexpected financial stress.
Companies that produce electric cars are now also experimenting with driverless technology on certain models of EVs, presenting an interesting challenge for the auto insurance industry. Currently, insurance companies are still evaluating how these features impact insurance premiums, as there are unique risks associated with these technologies, such as liability in the event of an accident while using autonomous driving modes. Owners of cars with autonomous driving capabilities should discuss these features with their insurance providers to ensure they have adequate coverage.
Take note that both hybrid and electric vehicles will come with a higher insurance premium than their traditional gas-powered counterparts. This is due to the advanced and often proprietary technology and parts used in the electric engine system, making it a lot harder to repair and source parts for these types of vehicles.
Pros & Cons of Hybrid vs Electric Cars
When it comes to hybrid vs electric cars, the pros and cons of each type are always a consideration for potential buyers. We’ve compiled a handy table that compares the advantages and disadvantages of each:
| Car Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Hybrid Vehicle | – Improved fuel economy and efficiency. – Reduced emissions compared to traditional vehicles. – No range anxiety due to the internal combustion engine backup. – Regenerative braking extends battery life. – Potential access to HOV lanes in some areas. – Lower upfront costs than most electric vehicles. | – Higher initial purchase cost than conventional cars. – Maintenance of both electric and internal combustion components can be complicated. – Less efficient in electric-only mode compared to full EVs. – In some cases, less cargo space due to battery placement. – Environmental impact from both fuel and battery production. – Potentially higher insurance costs due to more complex technology. |
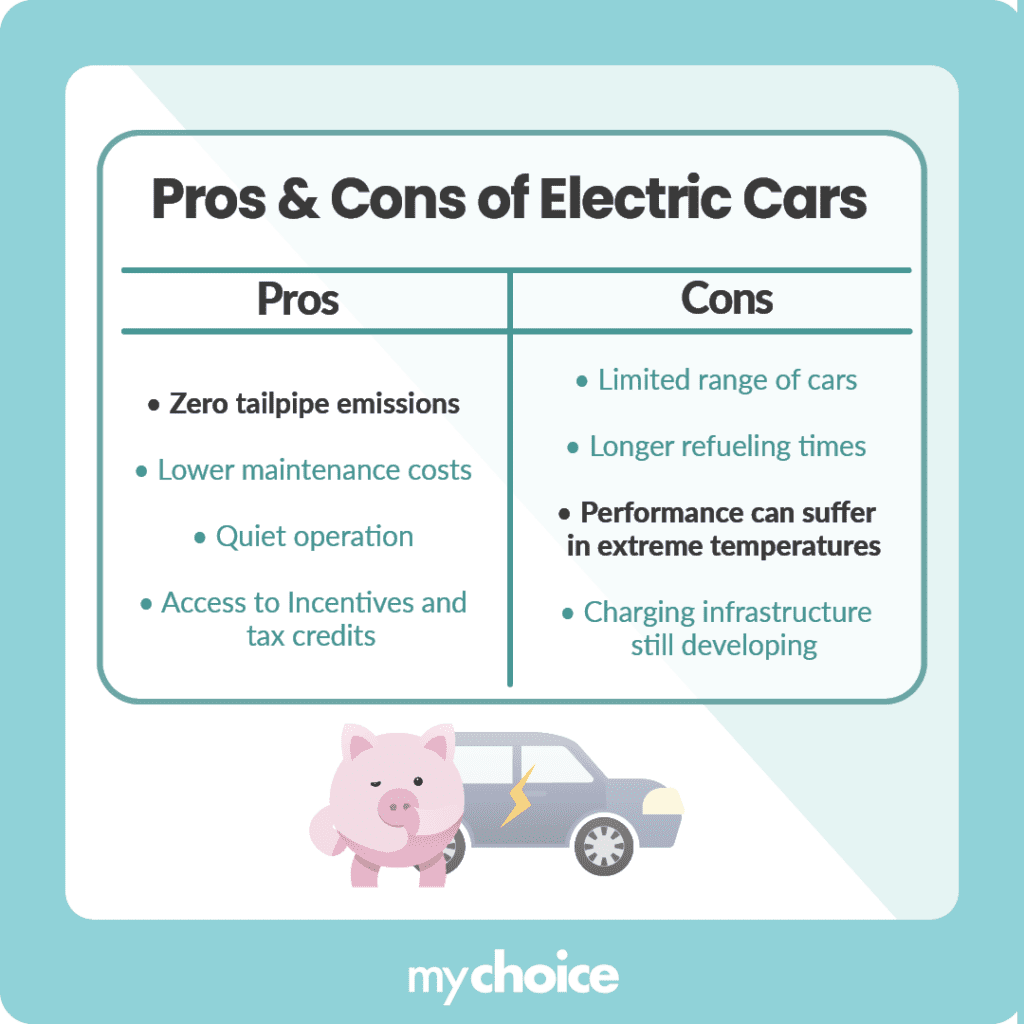
| Electric Vehicle | – Zero tailpipe emissions contribute to cleaner air. – Lower operating and maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts. – Instant torque and superior acceleration. – Quiet operation enhances driving experience. – Access to various incentives and tax credits. – Growing charging infrastructure minimizes range anxiety. | – Limited range compared to most gasoline cars. – Longer refueling times at charging stations. – Initial purchase price can be high for many models. – Battery replacement costs can be significant. – Performance can be affected by extreme temperatures. – Charging infrastructure is still developing in some regions. |

Performance in Extreme Weather
The harsh Canadian winters can pose significant challenges for both hybrid and electric vehicles, but each type responds differently to the extreme cold.
Electric vehicles are particularly vulnerable to freezing temperatures. The lithium-ion batteries that power EVs rely on the movement of lithium ions through an electrolyte. In cold weather, this movement slows down, leading to reduced energy output and range. EV owners in Canada can expect their vehicle’s range to drop by nearly 50% in extreme cold. Charging times also increase, as the battery management system needs to warm the battery before it can accept a full charge.
Hybrid vehicles, on the other hand, tend to perform better in cold conditions. Since hybrids utilize both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, they can rely on gasoline for power when the battery’s efficiency is compromised. This dual system allows hybrids to maintain better performance and range in freezing temperatures.
Innovations in EV Battery Technology
While the lithium-ion battery is the most widely used battery for both electric and hybrid vehicles, battery technology is advancing at a rapid pace. New battery types are being developed that promise to improve performance, range, and sustainability compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Traditional lithium-ion batteries currently dominate the EV market, offering a range of approximately 200 to 370 miles on a single charge, depending on the vehicle model and battery capacity. These batteries are well-established, but they face limitations in energy density and charging times, typically requiring 30 minutes to several hours for a full charge.
One of the most promising developments in battery technology is the emergence of solid-state batteries. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries that use liquid electrolytes, solid-state batteries utilize solid electrolytes, which can enhance safety by reducing the risk of leaks and fires. These batteries can potentially provide over 500 miles of range due to their higher energy density, which allows for more energy storage in a smaller and lighter package.
Another significant innovation is the development of silicon anode batteries. Traditional lithium-ion batteries typically use graphite as an anode material, which limits energy density. Silicon, on the other hand, has a much higher capacity for lithium ions, allowing for greater energy storage. Silicon anode batteries can increase the range of EVs to approximately 300 to 400 miles on a single charge.
Key Advice From MyChoice
- Hybrid vehicles can cost less to insure than purely electric cars, though both still command higher insurance premiums than traditional gas-powered cars.
- If you’re buying or leasing a hybrid or electric vehicle in Ontario, you’re eligible for a $5,000 incentive under the Incentives for Zero-Emission Vehicles (iZEV) Program.
- If you’ve installed a home charging system for your electric or hybrid vehicle, don’t forget to add that as an endorsement on your homeowner’s insurance policy.