Self-driving car technology has seen rapid advances in the last few years, with companies like Tesla and Mercedes leading the development of consumer-ready autonomous vehicles. While this technology is far from perfect, the science behind it is progressing quickly, with Mercedes claiming that an SAE level 4 autonomous vehicle will be commercially available within the decade.
The potential for self-driving cars to change the automotive industry is huge, but how will it affect your car insurance policy? Are driverless cars even allowed in Canada? Read on to learn all about driverless cars in Canada.
What Exactly Are Driverless Cars?
While you may imagine driverless cars to be purely automated cars that operate completely independent of its owner, the reality is a bit different. The Ontario Ministry of Transportation defines autonomous vehicles as “capable of detecting the surrounding environment using artificial intelligence, sensors and global positioning system coordinates.” This means that you’ll still need to pay attention and retain control of the vehicle, though you won’t need to full control all of its features.
These cars use a combination of sensors, radar, artificial intelligence, and machine learning algorithms to perceive their surroundings and navigate a road without the input of a human driver.
There are currently five levels of self-driving car, which are denoted by how much the driver needs to interact with the vehicle. These levels are:
At the moment, there are no cars that can operate at SAE levels 4 or 5, but many companies are racing towards developing a true self-driving car.
Are Driverless Cars Allowed in Canada?
At the moment, only two provinces in Canada allow the general public to ride driverless cars: Ontario and Quebec. In Ontario and Quebec, you can purchase and drive an autonomous car of SAE level 3 or lower, without needing to sign up for the Automated Vehicle Pilot Program, a specific government program that allows certain individuals to test out SAE level 4 and 5 vehicles. Since there currently aren’t any SAE level 4 or 5 cars available yet, this pilot program is largely meant for future applications as the industry evolves over time.
For the rest of Canada, self-driving vehicles are governed under the guidelines set by Transport Canada, though there are nuances for every province. For example, British Columbia has effectively ruled that driverless vehicles are not allowed on the road and don’t qualify for auto insurance. In Alberta and Nova Scotia, the rules regarding driverless cars are governed by the Traffic Safety Act, which can change over time as the technology for autonomous vehicles develops.
At the moment, your regular car insurance policy will cover automated vehicles in Ontario and Quebec, though do consult your insurance agent to make sure that you’re covered in case of an accident or theft of your vehicle.
How Did the Automated Vehicles Impact the Insurance Industry in the US?
The automated vehicle industry in the United States is fairly new, and insurance implications will continue to evolve over time as new legislation is decided on. At the moment, insurance companies in the US are still unsure of how to change existing policies or create new ones in regards to driverless vehicles, though the insurance market is preparing for sweeping changes in the coming years.
What Will Happen if Driverless Cars are Allowed in Canada?
If driverless cars become widely adopted in Canada, there will be big changes to road safety laws and insurance policies. Transport Canada is already monitoring the advancement of driverless car technology and is preparing to release updated guidelines as the technology becomes more prevalent.
A big industry that’s poised to take advantage of emerging autonomous vehicle technology is the transport industry. Trucks transporting goods throughout the country can stand to benefit hugely from the implementation of driverless technology, making them more efficient and cheaper to operate.
The United States has already seen driverless taxi services crop up in limited runs, and this sort of service can conceivably be offered in Canada soon. Fully automated taxis may soon become a reality for Canadians, which might cut down on transport costs.
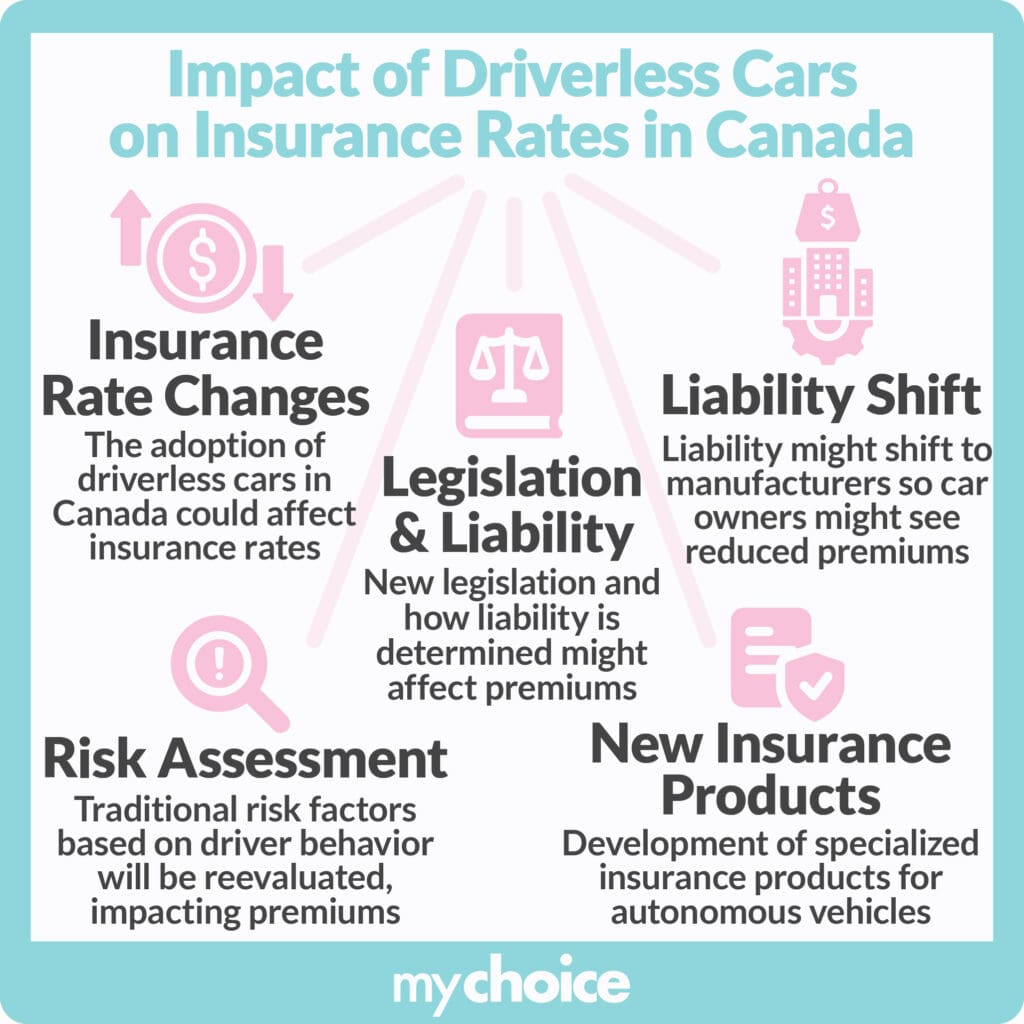
What Will it Mean for Your Insurance Rates?
Depending on how widespread driverless cars will be in Canada, your insurance rates can be heavily affected. If you choose to buy a driverless car, your insurance rates may change drastically depending on the legislation passed regarding driverless cars. The widespread adoption of automated vehicles can drastically change how fault is determined in a collision or accident, so this can affect who is liable in an accident.
Since the operation of a driverless car is largely dependent on the manufacturer and how they build and program their vehicles, you may see a reduction in your car insurance premiums as a result of liability shifting to the manufacturer in case of an accident.
Historically, the risk factor of the driver was used as the primary factor to determine insurance rates. With no human involved in the operation of a vehicle, insurance companies will have to figure out how their products will cover potential claims. However, this could also result in the creation of a whole new suite of insurance products designed specifically for autonomous vehicles.
The Insurance Bureau of Canada (IBC) has released a report entitled “Auto Insurance for Automated Vehicles: Preparing for the Future of Mobility” that gives three recommendations for insurance companies as driverless car technology becomes more accepted. These recommendations are:
- Establish a single insurance policy covering driver negligence and the automated technology to facilitate liability claims.
- Establish a legislated data-sharing arrangement with vehicle manufacturers and vehicle owners and/or insurers to help determine the cause of a collision.
- Update the federal vehicle safety standards with technology and cyber security standards.
Key Advice from MyChoice
- Keep an eye on the regulatory changes. Currently, only Ontario and Quebec allow SAE level 3 driverless vehicles to be bought and operated by the general public. Future legislation will evolve along with the technology used in driverless vehicles, affecting costs, liability, and other insurance factors.
- Consult with your broker, as the insurance rates and products may see a drastic change if driverless vehicles become widely adopted in Canada.