Accident benefits play an essential role in Ontario car insurance. They can provide the appropriate compensation if you are hurt or killed in an automobile accident.
Paying for healthcare expenses is the last thing you want to worry about when recovering from a car accident. Learn how accident benefits can give you peace of mind.
What Are Accident Benefits?
Accident benefits provide monetary compensation if you, passengers, or pedestrians are injured in a car accident. This coverage applies regardless of who caused the accident and can cover medical expenses, lost income, and other accident-related costs. Accident benefits are mandatory in Ontario as part of the minimum auto insurance requirements.
Who is Covered by Accident Benefits in Ontario?
In Ontario, accident benefits extend to the following individuals:
- The driver of the insured vehicle, even if they were at fault
- Passengers in the insured vehicle
- Injured pedestrians or cyclists
- Occupants of cars with no-fault insurance
In case of the driver’s death, their dependents may be eligible for financial benefits.
What Happens if You Are at Fault?
Because Ontario enforces a no-fault accident system, causing a vehicular accident doesn’t directly impact your ability to receive compensation. However, you may receive reduced benefits.
Your insurance company can reduce your benefits depending on the degree of fault (from 1% to 99%). In addition, renewing your policy when you are at fault may increase your premiums as you’ll be considered a high-risk driver.
Types of Accident Benefits Coverage in Ontario
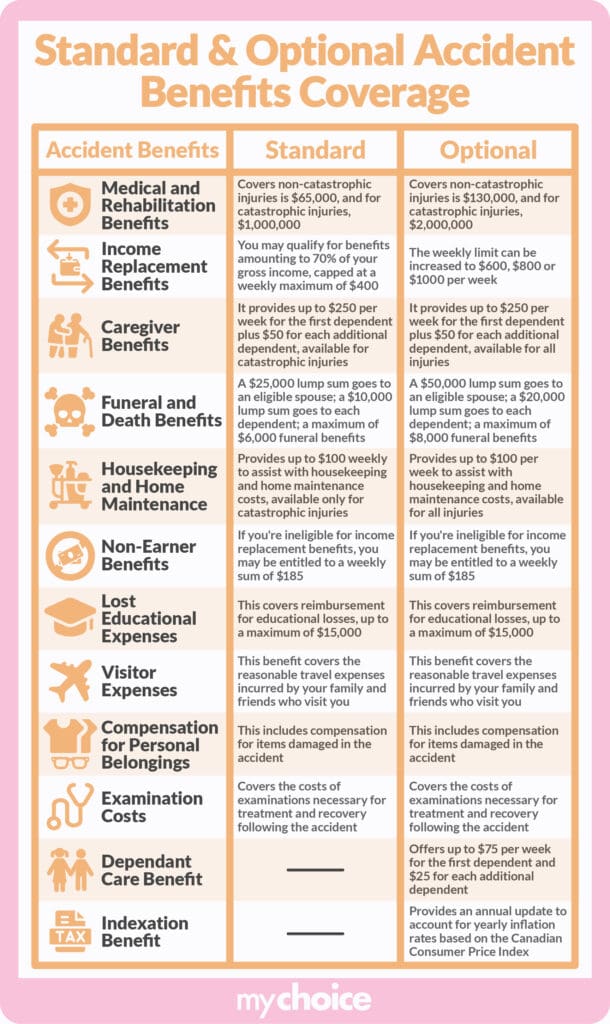
Ontario’s two primary categories of accident benefits are mandatory and optional. Understanding the differences can help you make more informed decisions about your insurance.
Below is the graphic with the detailed comparison between standard and optional benefits.
Why Consider Optional Accident Benefits?
Though mandatory benefits already provide ample financial coverage, there are several reasons why you might consider optional benefits:
- Your injuries are extensive, or mandatory benefits can’t finance a full recovery.
- You rely heavily on your income.
- You have a pre-existing condition that can complicate the recovery process.
- You need support for your loved ones.
- You develop a permanent disability or condition.
Look at it this way: Mandatory benefits are like basic first aid kits, whereas their optional counterparts act as comprehensive medical kits.
Accident Benefits Comparison Between Provinces
Accident benefits coverage can vary significantly across Canadian provinces. Here is a breakdown of the differences to consider.
Private vs. Public
In provinces like Ontario and Nova Scotia, you can select your insurer and coverage level from private insurance markets. Conversely, provinces like Manitoba and British Columbia have public systems with standardized benefits.
However, private institutions don’t always offer higher coverage. For example, Ontario, which has private insurance, has a coverage standard of $65,000 with an upper limit of $1 million, while British Columbia (public) and Quebec (unique system) don’t have set limits. In addition, Ontario has an income replacement ceiling of 70%, whereas Quebec’s ceiling is 90%.
Optional Coverage Availability
While all Canadian provinces provide optional accident benefits, coverage availability often varies. For example, Ontario has many coverage options, including increased medical and caregiver benefits. On the other hand, optional coverage in British Columbia is minimal.
Step-by-Step Accident Claim Process
Making a car accident claim in Ontario is relatively straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step look at what you should do after an accident.
Immediately After the Accident
The first thing you should do after a vehicular accident is ensure your safety. Check for injuries to yourself and other passengers and immediately report the car accident to 911. If it is safe, move your vehicle out of traffic to prevent other collisions.
Then, gather as much information as possible, including the following:
- Contact details and insurance information of involved drivers and injured people
- Photos of the accident scene
- Names and contact details of any witnesses
- Date, time, and location of the accident
- A description of the accident
- Extent and photos of injuries
- The name and badge number of the investigating officer
Within a Week
Report the accident to your insurance provider as soon as possible, providing all the information you gathered. File the necessary documents to make a claim.
Your insurance company will determine fault according to the Insurance Act and Fault Determination Rules.
After Making a Claim
Making a claim is far from the last step of your insurance journey. You must be prepared to follow up with additional information regarding the accident and gather medical documentation. The insurance company can assess medical expenses based on medical reports, receipts, and other documents.
If you feel the offer is inadequate, you can negotiate your claim. However, the process can get complicated, so you’ll want to consider hiring a personal injury lawyer for support.
Drivers can resolve disputes through the Licence Appeal Tribunal.
Coverage Denial
Under the following circumstances, your insurance company has the right to deny compensation replacement and other benefits:
- You were driving without valid insurance.
- You don’t have a valid driver’s licence.
- You were driving a vehicle without the owner’s consent.
- You were driving the vehicle while committing a crime.
- You provide insufficient evidence, such as a lack of medical documentation and unclear accident details.
- You’ve intentionally provided false information about the accident and your injuries.
- You miss filing deadlines.
Key Advice from MyChoice
Vehicular accidents can be a traumatizing experience, but knowing how to report and manage an accident claim can provide the benefits and compensation you deserve. Here are a few other points to remember from MyChoice:
- Understand the differences between mandatory and optional coverage to determine whether you require greater financial protection.
- Act quickly after an accident, collecting as much information as possible. Report the incident to your insurance provider within seven days.
- While being at fault doesn’t prevent you from filing a claim, understanding how it may impact your benefits is imperative.